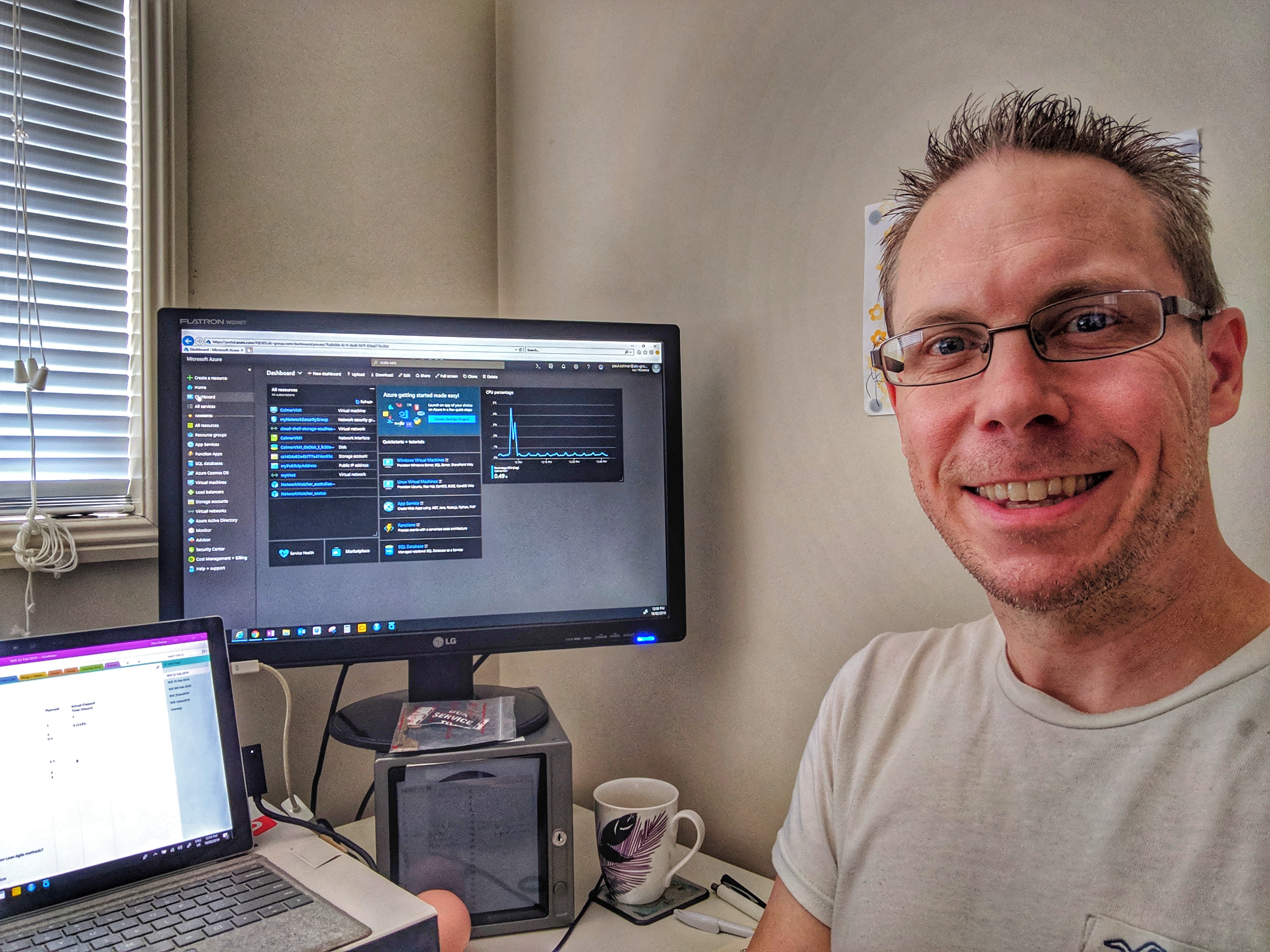
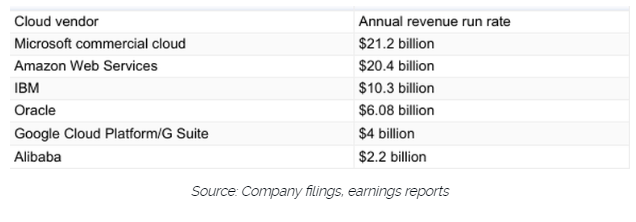
Microsoft is one of the world leaders when it comes to cloud computing services. In the last comparison of revenue streams from the cloud giants, back in Feb 2018, it seems that Microsoft was just ahead in front of AWS.
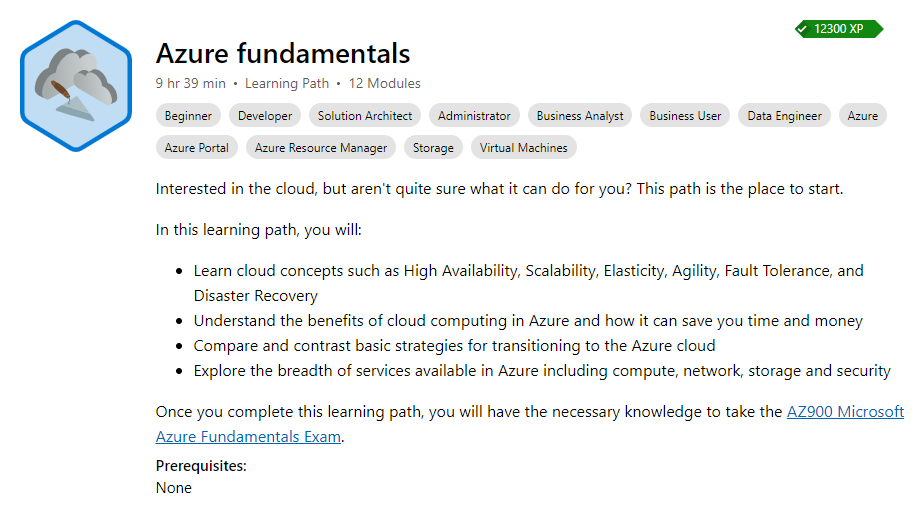
Want to learn more about Azure? Well, there are options. There is a great free resource from Microsoft that covers Azure fundamentals here:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/learn/paths/azure-fundamentals/
Or, if you’re looking for more a hands-on 1 Day Azure Technical Quickstart to understand how to provision resources, you can check out our 1 Day course here:
https://alctraining.com.au/course/microsoft-azure-technical-quickstart/

You can also reach out to us, for customised Azure and Office 365 courses.
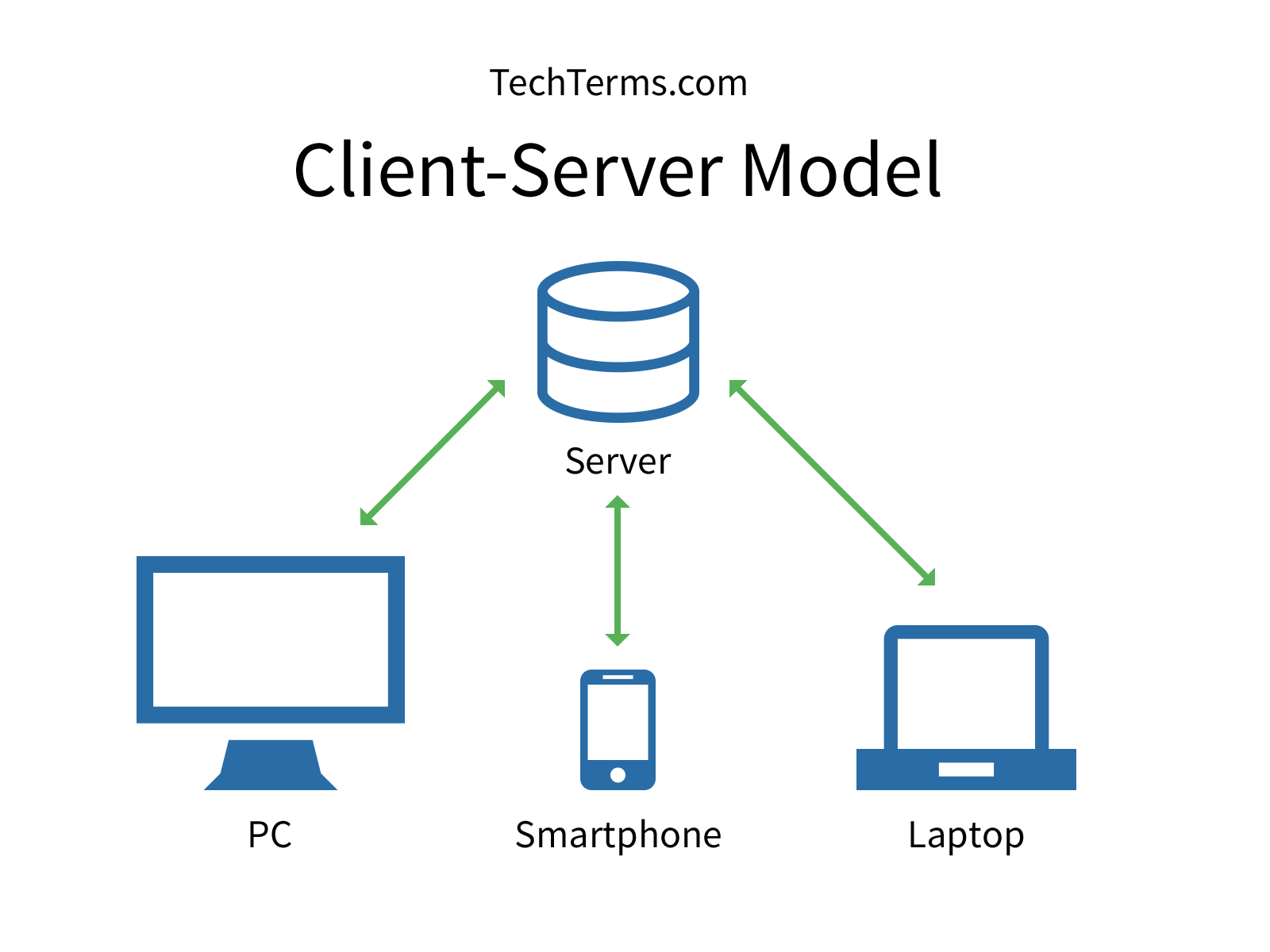
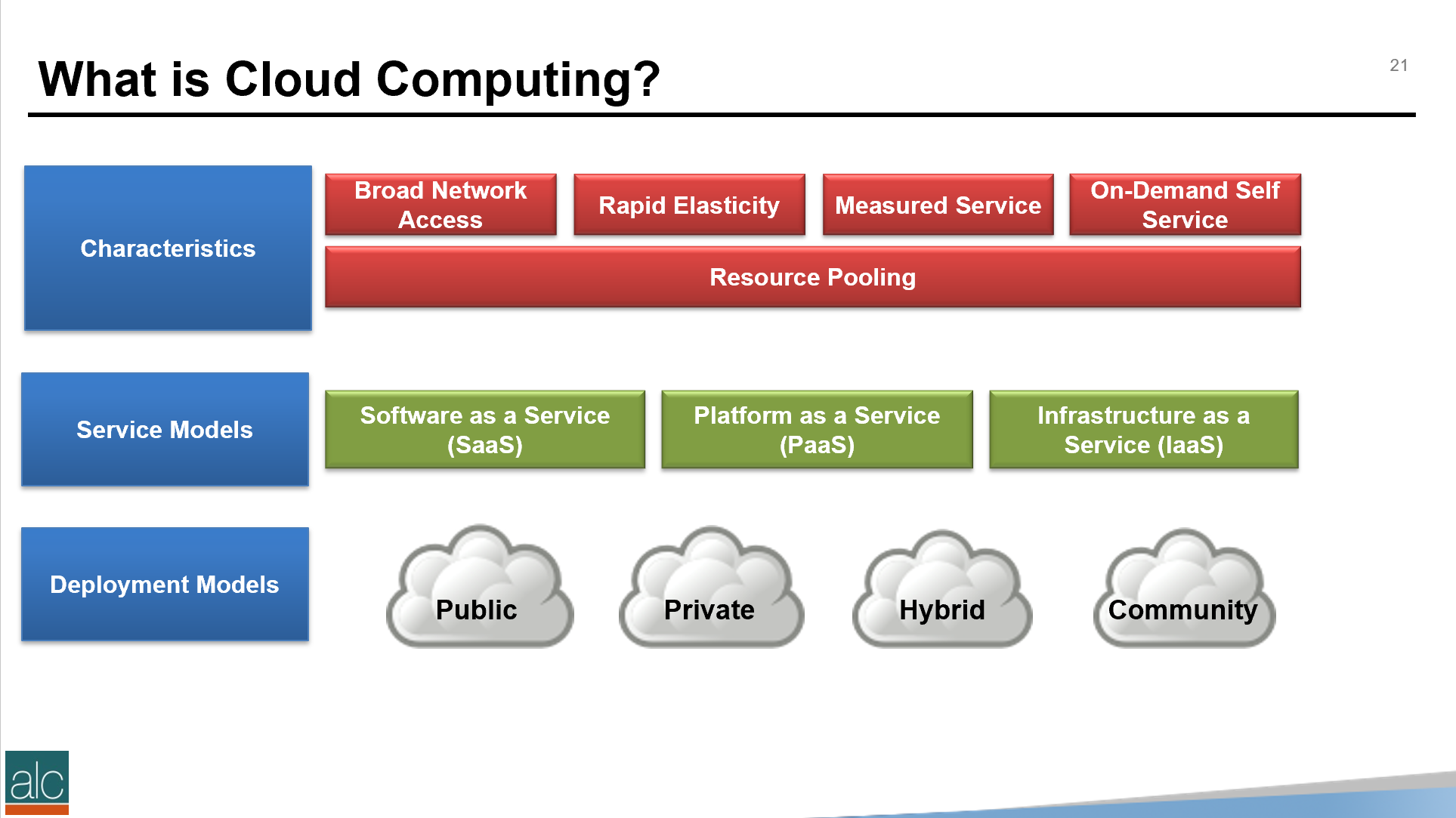
Azure is classed as an Infrastructure-As-A-Service (Iaas) and Platform-As-A-Service (PaaS) in the cloud computing world. IaaS services are designed for system engineers, where you can set up and build servers, networks, and storage, and then install your apps on top. If you’re in the software development business, then the PaaS services are designed for writing, testing and managing code, and target developers.
Some important PaaS services that developers will need include:
- Source Code Repositories – Such as GitHub or Azure Repos – these allow you to store and version control your source code.
- Serverless – Azure Functions – automatically builds and manages the compute, storage and networking components, so a developer can focus on writing code.
- Containerisation – Azure Kubernetes Services – allows developers to build, manage and monitor containers, which are used to store separate app stacks, relating to separate apps.
- Datastores – Azure SQL or Azure Cosmos DB – allows developers to store and read structured (SQL) and unstructured data.
Below is a brief snapshot of just the Compute services:
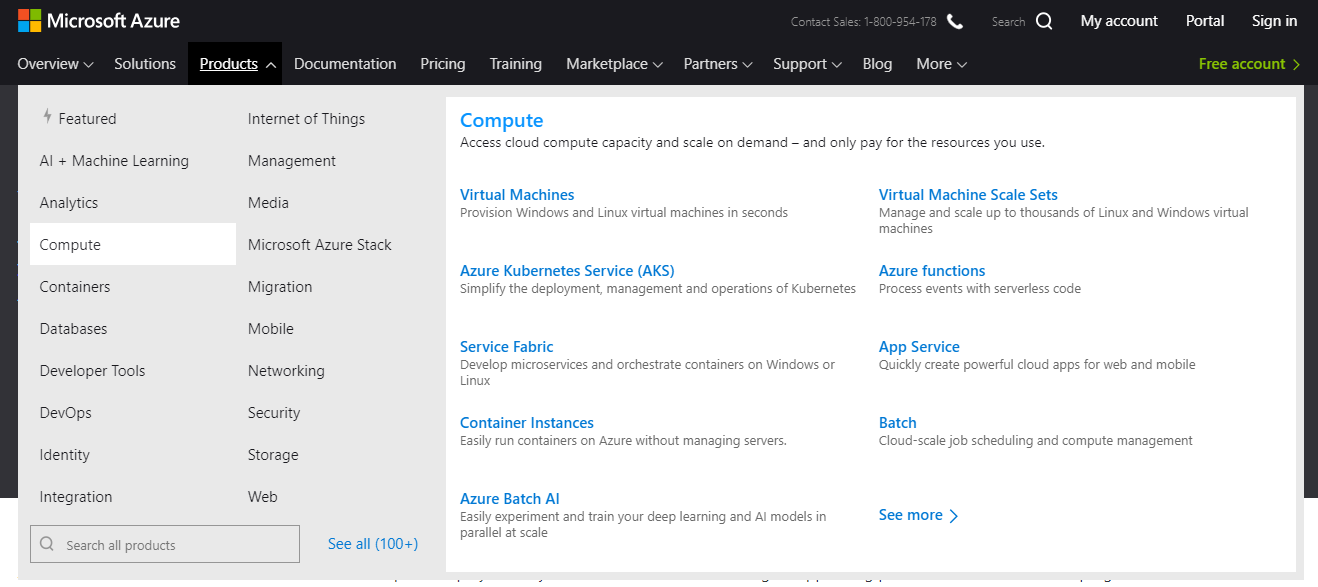
By combining together these services, you can create a rich tapestry of solutions. It’s very similar to the age of analog electronics, where you could select oscillators, diodes and specific electronics components, to create solutions like creating a home radio.
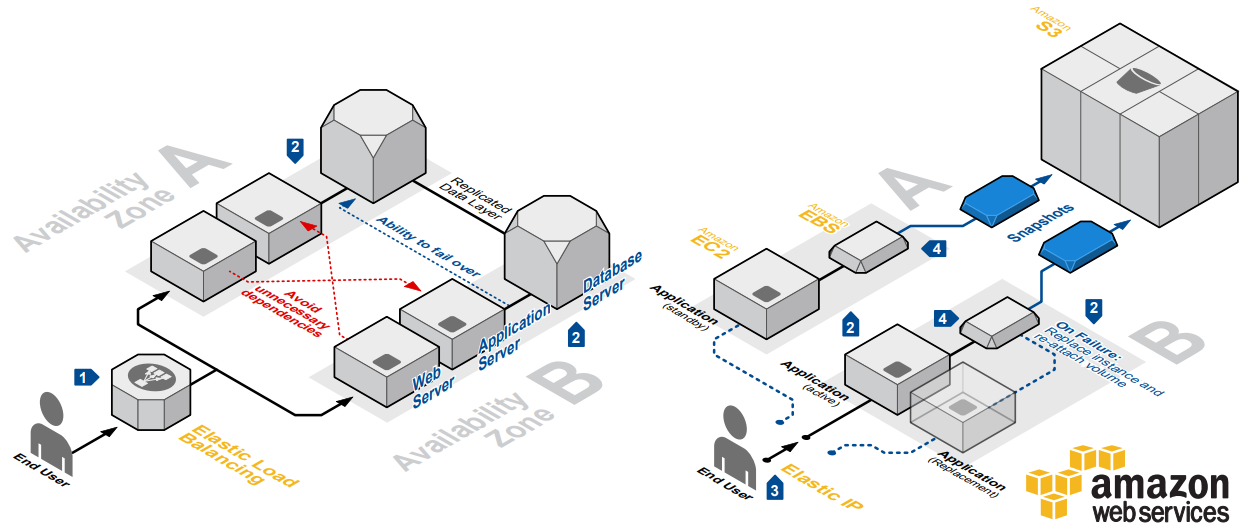
In Azure you can create very complex business solutions. Below is an example of how you might integrate a complex corporate environment with Azure services, in a model known as hybrid cloud:
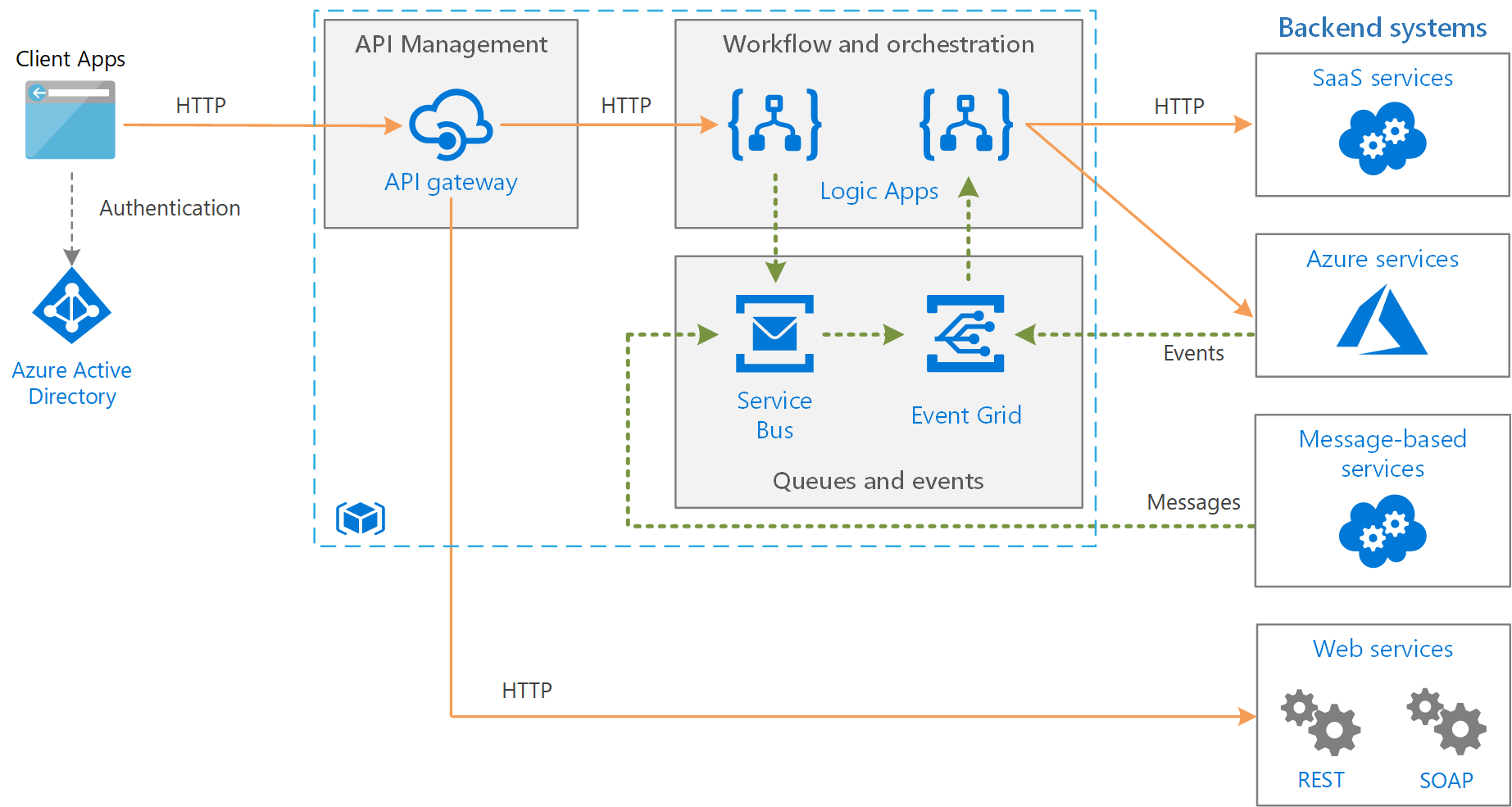
There are some very important services that are available in Azure, that align nicely to medium to large clients that have to comply with complex regulation. Clients involving in banking, government, healthcare, and defence, need to maintain a level of corporate and regulatory governance, as well as a high level of cyber security protection in their cloud services. Tools such as:
- Azure Security Centre – understand, see and manage your security across all your Azure resources. Very useful when dealing with a critical security incident in your organisation.
- Azure Advanced Threat Protection – Protect your assets from all kinds of threats, both inside and outside your organisation, using AI and smart analytics.
- Azure Policy – Enforce rules across how and where your Azure resources are deployed. Need to only deploy in Australia, no problem, set up a policy that only allows services to be run from Australia.
- Azure Blueprints – Setup standard collections of resources, pre-approved by your security and governance functions that allow fast deployment of business solutions.
- Azure Monitor – Monitor the health of all the resources you have created and have control over.
- Azure Service Health – Monitor the health of all the resources that Microsoft controls.
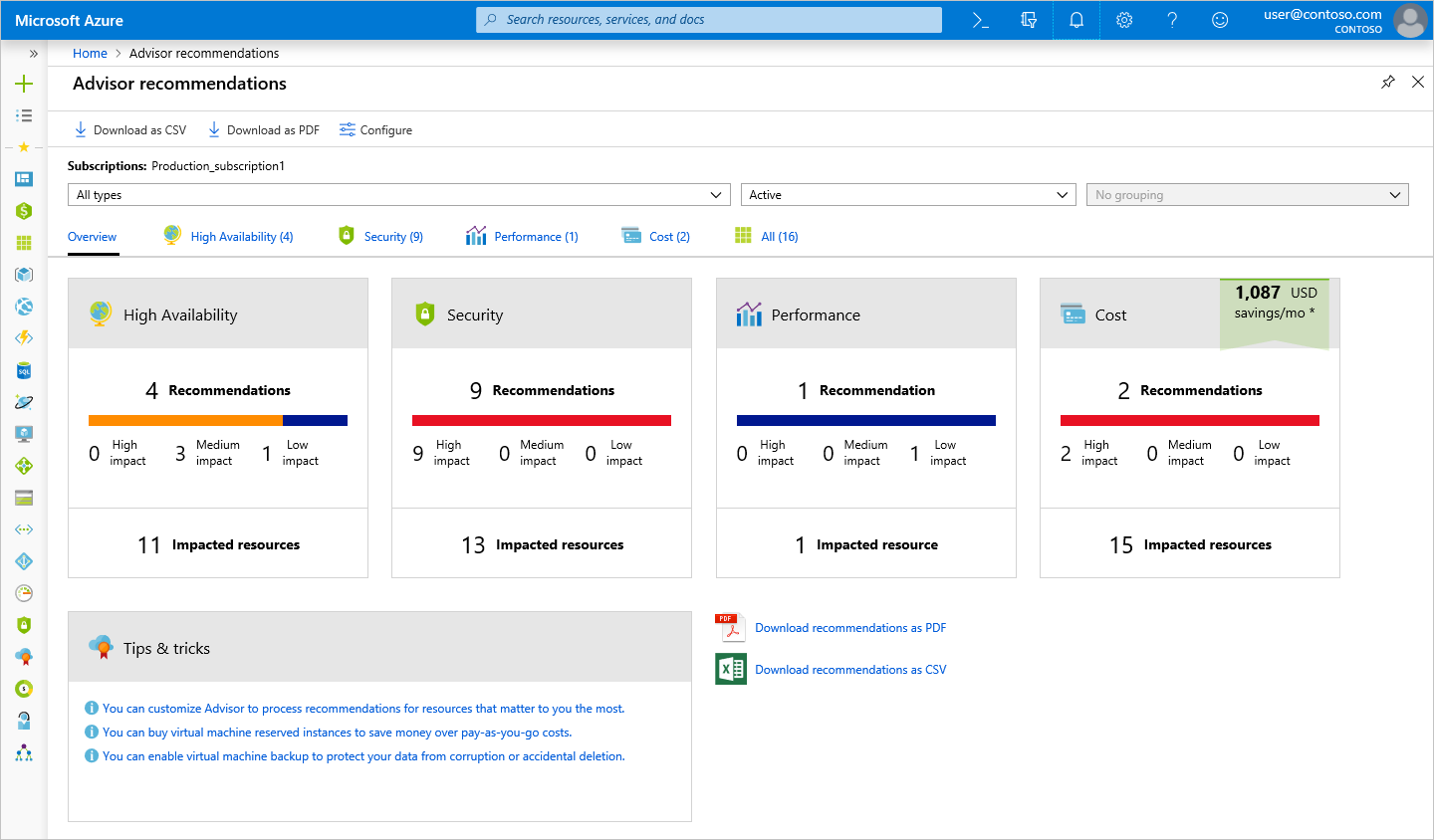
- Azure Advisor – Makes intelligent recommendations covering Availability, Security, Performance, and Cost.
The diagram below shows an example of the types of recommendations that the Azure Advisor can provide:
Feel free to reach out anytime with your Azure of Office 365 questions or queries?